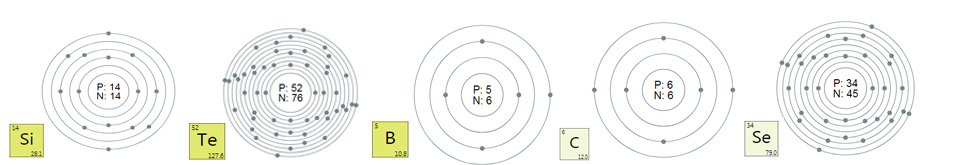
tellurium
Tellurium Ingots & ndash; presented in crystalline
form, has a silvery-white shiny color. Refers to semimetals, outwardly
similar to antimony and tin. It is very fragile, due to which it can be
easily crushed. Melting point 449.8 ° C. It dissolves in alkalis, lends
itself to the action of nitric and sulfuric acids. In chemical compounds
with non-metals, tellurium exhibits similar properties to selenium and
sulfur.
Tellurium, like selenium, is produced commercially exclusively from the
by-products of large-scale electrolytic copper and nickel production.
Main areas of application:
1. Alternative energy & ndash; production of solar panels. Tellurium is
doped with cadmium to produce cadmium telluride, which is used in
photovoltaic thin-film solar panels. For today & ndash; it is the
largest consumer of tellurium in the world
2. Metallurgy: used as an alloying additive in the production of
lead-tellurium alloys, which are used in cable and chemical industries.
Alloy with tellurium, also copper and steel to facilitate their
machining
3. Glass and rubber production. Tellurium (in the form of dioxide) is
used in the melting of special types of glass, which are used as active
bodies of optical quantum generators. In addition, some tellurium-based
glasses are semiconductors, which favors their use in electronics. Also,
tellurium compounds are used in rubber vulcanization.
4. Microelectronics. The compound of tungsten and tellurium is a
ferroelectric & mdash; one of the 'materials of the future'. This alloy
can become a unique basis for ultra-efficient computers, and can also be
used as a `` memory of the future '', where information will be recorded
in the form of a combination of similar electrons.
.

Tellurium Ingots & ndash; presented in crystalline
form, has a silvery-white shiny color. Refers to semimetals, outwardly
similar to antimony and tin. It is very fragile, due to which it can be
easily crushed. Melting point 449.8 ° C. It dissolves in alkalis, lends
itself to the action of nitric and sulfuric acids. In chemical compounds
with non-metals, tellurium exhibits similar properties to selenium and
sulfur.
Tellurium, like selenium, is produced commercially exclusively from the
by-products of large-scale electrolytic copper and nickel production.
Main areas of application:
1. Alternative energy & ndash; production of solar panels. Tellurium is
doped with cadmium to produce cadmium telluride, which is used in
photovoltaic thin-film solar panels. For today & ndash; it is the
largest consumer of tellurium in the world
2. Metallurgy: used as an alloying additive in the production of
lead-tellurium alloys, which are used in cable and chemical industries.
Alloy with tellurium, also copper and steel to facilitate their
machining
3. Glass and rubber production. Tellurium (in the form of dioxide) is
used in the melting of special types of glass, which are used as active
bodies of optical quantum generators. In addition, some tellurium-based
glasses are semiconductors, which favors their use in electronics. Also,
tellurium compounds are used in rubber vulcanization.
4. Microelectronics. The compound of tungsten and tellurium is a
ferroelectric & mdash; one of the 'materials of the future'. This alloy
can become a unique basis for ultra-efficient computers, and can also be
used as a `` memory of the future '', where information will be recorded
in the form of a combination of similar electrons.
.

|
|